TOP-UP YOUR SUPER WITH HELP FROM THE GOVERNMENT
If your income is under a certain threshold, then making personal after-tax super contributions could enable you to qualify for a Government co-contribution and take advantage of the low tax rate payable in super on investment earnings.
HOW DOES THE STRATEGY WORK?
If you earn¹ less than $52,698 pa (of which at least 10% is from eligible employment or carrying on a business) and you make personal after-tax super contributions, the Government may also contribute into your super account. This additional super contribution, which is known as a co-contribution, could make a significant difference to the value of your retirement savings over time. To qualify for a co-contribution, you will need to meet a range of conditions, but as a general rule:
The maximum co-contribution of $500 is available if you contribute $1,000 and earn $37,697 or less
A reduced amount may be received if you contribute less than $1,000 and/or earn between $37,697 and $52,697 and
You will not be eligible for a co-contribution if you earn $52,697 or more.
The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) will determine whether you qualify based on the data received from your super fund (usually by 31 October each year for the preceding financial year) and the information contained in your tax return.
As a result, there can be a time lag between when you make your personal after-tax super contribution and when the Government pays contribution and when the Government pays the co‑contribution.
If you’re eligible for the co-contribution, you can nominate which fund you would like to receive the payment. Alternatively, if you don’t make a nomination and you have more than one account, the ATO will pay the money into one of your funds based on set criteria.
Note: Some funds or superannuation interests may not be able to receive co-contributions. This includes unfunded public sector schemes, defined benefit interests, traditional policies (such as endowment or whole of life) and insurance only superannuation interests.
OTHER KEY CONSIDERATIONS
You can’t access super until you meet certain conditions.
You may want to consider other ways to contribute to super, such as salary sacrifice or personal deductible contributions.
CASE STUDY
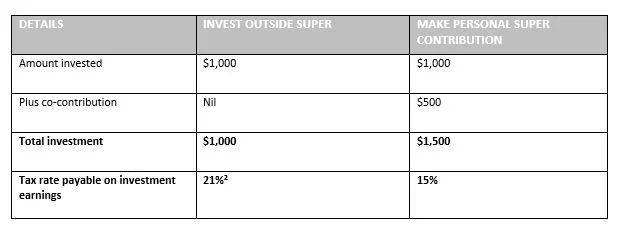
Ryan, aged 40, is employed and earns $35,000 pa. He wants to build his retirement savings and can afford to invest $1,000 a year. After speaking to a financial adviser, he decides to use the $1,000 to make a personal after-tax super contribution.
By using this strategy, he’ll qualify for a co-contribution of $500 and the investment earnings will be taxed at a maximum rate of 15%. Conversely, if he invests the money outside super each year (in a managed fund, for example), he will not qualify for a co-contribution and the earnings will be taxable at his marginal rate of 21%.²